After spending hours watching stock market videos on YouTube and much discussions with colleagues, Parth decided to invest in the stock market hoping to make a huge fortune from it. Unfortunately, Parth learnt that those stocks failed to perform in the market as per the expectations and some stocks did not deliver the returns as estimated. He wondered what might have possibly gone wrong since a thorough study of fundamentals and research on basic details such as revenues, net profit, earnings per share (EPS), and price to earnings ratio (PE ratio) was done.
What happened to Parth is not a rare case. Many new investors decide to plunge into the stock market game on receiving tips and rumours and invest blindly. Being aware of the fundamentals as announced by the company in the quarterly report is not sufficient to trade. This is where the importance of reading the annual report steps in as it contains plenty of company information that is not available otherwise. It is a bulky report of 180-200 pages consisting of jargons that become an ordeal for an investor. At times, the pertinent content gets hidden making investors simply skip through the pages and invest based on the face value of a company. But, here we will talk about the essentials of the annual report that every investor should be looking into because knowing the fundamentals is not enough.
‘‘
Potential investors and existing shareholders form the primary audience for the annual report. For an investor, the reports contain relevant information about a company in its truest form.
What is an annual report?
It is a yearly publication that is published by the company at the end of the financial year which is sent to shareholders and other interested parties. The information available in the report is dated till 31st March. It is also available on the company’s website as a PDF file which can be downloaded.
The information mentioned in annual reports is taken to be official. Hence, any twisting or misrepresentation of facts in the annual report can be held against the company. It also contains auditor’s certificates indicating the authenticity of the financial data in the report.
How is an annual report helpful to investors?
Potential investors and existing shareholders form the primary audience for the annual report. For an investor, the reports contain relevant information about a company in its truest form. Several news sites and blogs throw abundant information that can be rumours or biased views which in turn impacts an investor’s ability to invest in the right stocks. Information gathered about a company is more reliable from its annual reports.
Here are some of the ways it can be helpful to the investor:
- Comes straight from the horse’s mouth.
- Gives an idea of the management sentiment
- The cleanest source of data
- Considered as the official statement of the company
What to look for in an annual report?
An investor does not need to read an entire lengthy document. Here is a guide that will help the investor to look for 8 important parameters to analyse while reading an annual report.
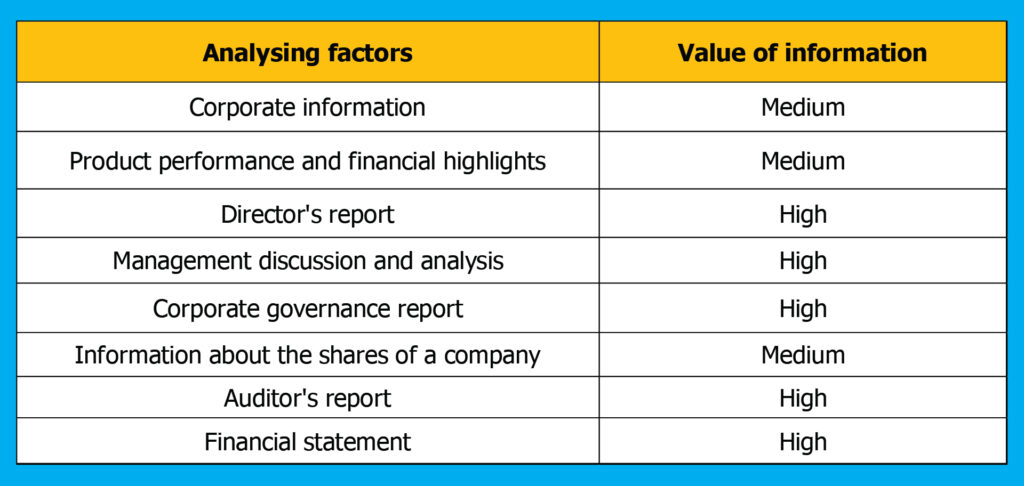
Corporate information:
One can get the details of directors, bankers, auditors of the registered and corporate office. Here, investors need to look at the designation of each board member, in the case of reputed auditors they can add certain reliability to the company they are investing in.
Products and financial highlights of last 5-10 years:
Investors can get information regarding the performance of a company’s entire product portfolio based on fundamentals such as revenue, EBIT, depreciation, and amortisation, tax, PAT (net income) and profit and loss. They can also get a glimpse of shareholders’ equity, assets, debtors, liability, and total debt from the balance sheet over the years and ratios.
Director’s report:
From this, investors can get a summary of the financial results and key developments in the company. Investors should look for the operational parameters such as capacity additions, capex plan, order book till the financial year-end, the average length of stay, occupancy rates, average revenue per occupied bed, average revenue per user, etc. Also, read the director’s report of 3-5 years to see if the management is consistent regarding achieving the targeted revenue over the years.
Management discussion and analysis (MDA):
It provides information on the trends of the industry. The SWOT analysis of the company will make one aware of risk factors impacting the performance. It is suggested to read 3-5 years of MDA to understand how the company has remained resilient in different economic scenarios.
Corporate governance report:
Provides insight regarding corporate governance since good governance makes operations and running of a business efficient. Look for the composition of the board of directors, brief background information on directors and independent directors of the company, attendance of directors in board meetings and annual general meetings, remuneration of directors, re-appointment of directors after completing the term, the composition of sub-committees, etc. Analyse if the profile of independent directors aligns with the requirement of the company as per sector of a company.
Information on shares of the company:
This is a highly valued one for the investors. In this section, a company shares information on the historical performance of share price, shareholding pattern of the company, pledging of shares by promoters during the year, split of shares, bonus shares distributed, etc.
Auditors report:
Provides information regarding the feedback of auditors on the financials of the company.
Financial statements:
Provides detailed information regarding profit and loss accounts, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and schedules of the financials for two years. Analysing these parameters will help us in checking the financial health of the company.
Below is a table that shows which factor in the annual report holds how much value.
Don’t fall into the trap of empty promises
An annual report can sometimes exaggerate the data to make it look promising to the investors. It is understandable that is an official document of a company and is less likely to publish false numbers, but in case if you find numbers misrepresented, always check by looking into the following:
- Large cash flows: Companies with large cash flows indicate healthy business.
- Continuity in business: Checking for continuity means comparing each figure with the preceding years to understand how the company has done. If any figure is higher or lower than the previous year, find the reasons behind the jump or fall instead of assuming it.
- Actual sales: Calculate all the four quarters of sales data to see if it matches the annual sales figure. An alternative to look at the sales will be checking sales growth with the increase in debt because a higher debt rising with sales means the company is giving away goods without collecting money.
- Real profit: Similar to sales, investors need to cross-check the net profit figure because the price to earnings (PE) ratio is the most commonly used valuation tool. Companies manipulate the profit figure by providing for excessive (or even less) depreciation.




