Dividend payout is the ratio of the total amount in dividends paid out to shareholders to a company’s net profit. The dividend return is paid to shareholders from portions of a company’s profits. The dividend payout ratio is sometimes referred to as the payout ratio.
Companies use the unpaid dividends or leftover profits for numerous corporate tasks, including debt settlement and reinvestment in the business. When a company makes good profits, it can choose to distribute those gains to shareholders in the form of dividends. Investors calculate the percentage of profits used for dividend payouts to common shareholders using the Dividend payout ratio.
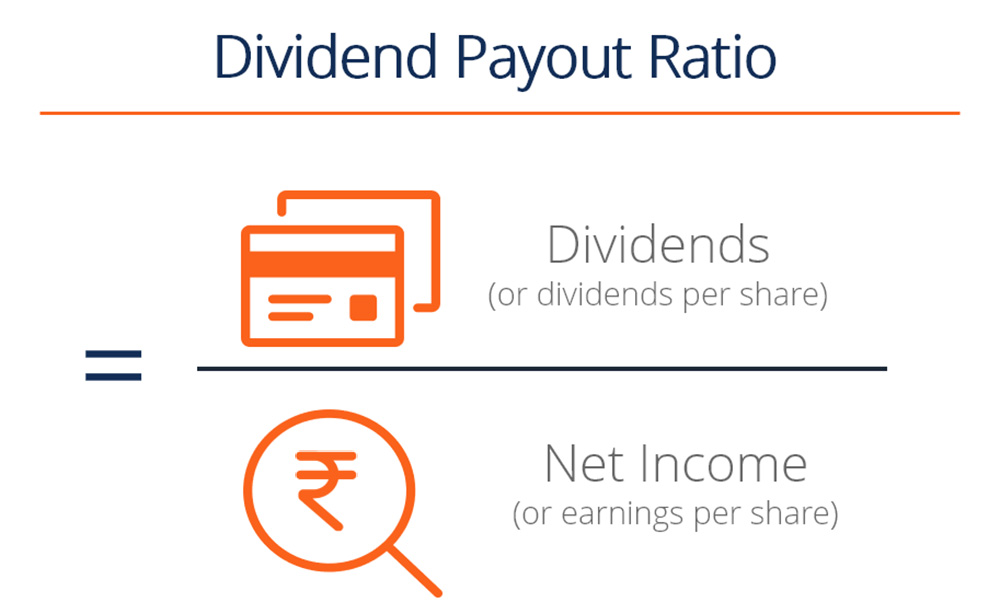
This ratio is calculated by dividing the dividends per common share with earnings per share (this information is included in the company’s income statement). Dividing the dividends per common share by the earnings per share gives the dividend payout. The result is the percentage of profits that dividends compose.
There are two major benefits of knowing this percentage:
- For investors looking for a stable return on their investment, dividend payout ratios are an integral part of their investment strategy.
- The ratio of earnings that companies pay out in dividends reflects their growth plans. A low dividend payout with no expansion may show trouble; the same is true for a high dividend payout in a growing company.
Example of the Dividend Payout Ratio
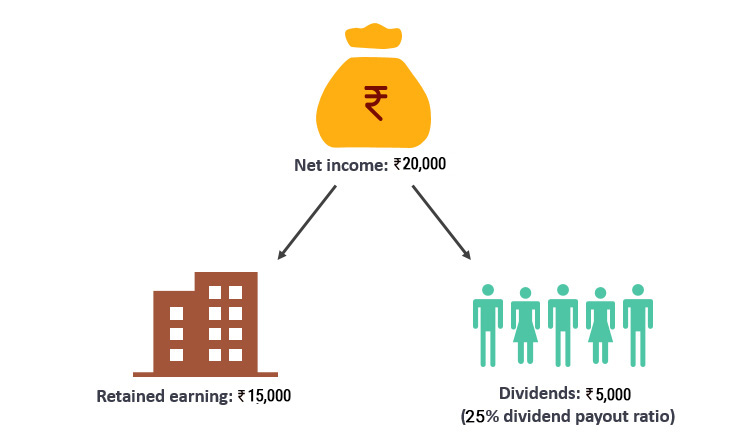
Assume that Company XYZ’s annual net earnings per share are Rs 20,000 per share. In this time, the company declared and paid dividends to shareholders of Rs. 5,000 per common share. The dividend payout ratio (DPR) is calculated as follows:
Dividend Payout Ratio = Rs. 5,000 / Rs. 20,000 = 25%
Therefore, a payout percentage of 25% means that Company XYZ pays out 25% of its net income to shareholders. The remaining 75% of net income kept by the company for growth becomes its retained earnings.
Often larger or non-operational companies have higher dividend payout ratios, while smaller or larger companies retain those earnings for future growth.
Calculating the dividend yield is critical for investors concerned with the amount of income they will generate from the dividends on their stock. This metric tells how much income they will develop in the form of bonuses for their price on each share of stock.
Dividend yield
By comparing the dividend yield of different companies, you can decide if you will get a competitive dividend price based on the stocks.

Here is how to use this equation. Look for dividends per common share at the bottom of a company’s earnings report and check the stock equities market. You can also have your broker calculate the market price per share.
Divide the dividends per common share by the market price per common share to calculate the dividend yield.
Dividend yield determines the percentage of value an investor pays for his shares issued in the previous year’s dividends. Remember that the number of dividends paid out each year can vary, meaning dividend income may not be reliable unless the company you are examining pays the same dividends every year historically.
Difference between dividend yield and dividend payout ratio
In comparing these two parameters, it is essential to note dividend yield highlights the simple rate of return in the form of cash dividends to shareholders. On the other hand, the dividend payout ratio refers to the amount of profit that a company pays in dividends.
What more does the dividend payout ratio tell?
The dividend payout ratio is the most crucial metric used to determine the profitability of a company’s dividend payment program. It is the number of dividends paid to shareholders relative to the total net income of a company.
Diligent and active investors do not always seek high dividend payout companies to invest in. An unusually high dividend payout ratio indicates that the company is trying to hide its activities by providing more dividends to investors or by not thinking about using the capital in any way for growth.




