The Fourth Industrial Revolution aka Industry 4.0, as the German government coined the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technology, signals a series of social, political, cultural, and economic disruptions that will unfold over the contemporary 21st century.
Building on the widely spread global availability of digital technologies that were the results of the Third Industrial, or Digital, Revolution, which again were the contributions of the proceeding industrial revolutions, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is and will be driven largely by the convergence of digital, biological, and physical innovations.
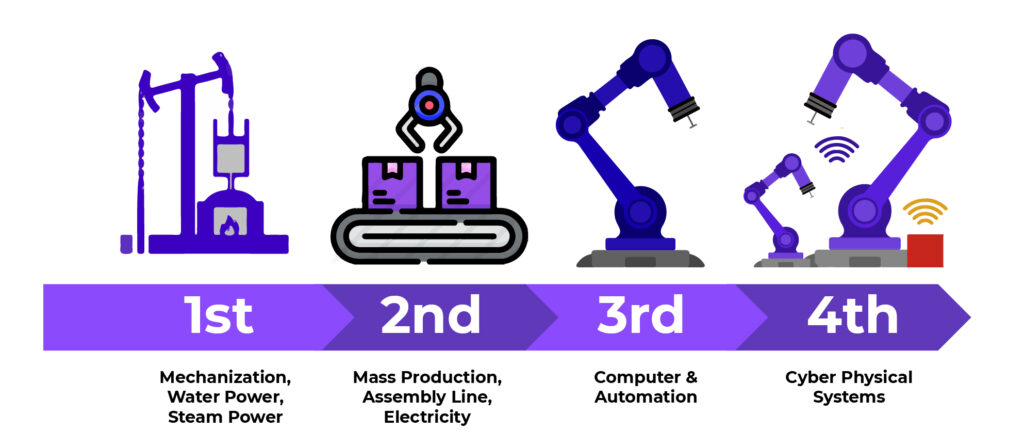
Evolution of Industrial Revolutions
The four industrial revolutions contributed coal, gas, electronics, nuclear, transport, and the internet, digital and renewable energy. As we discovered in recent times, with the advancements in different energy sources and later, digital technologies, the entire landscape of the modern world has been transformed over and over. The ongoing pandemic has again accelerated its advancements out of the need for sustenance. Before we dive into the Fourth Industrial Revolution, here is a brief primer on the first three industrial revolutions.
“We must develop a comprehensive and globally shared view of how technology is affecting our lives and reshaping our economic, social, cultural, and human environments. There has never been a time of greater promise, or greater peril.” – said Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman, World Economic ForumThis is one of the best quotes I have across so far on Industry 4.0.
First Industrial Revolution
The original or the first industrial revolution, which is estimated to have begun in 1765, transformed the world economy from agriculture to industry. Products were manufactured for the first time using mechanized processes. During this period, the discovery of coal and its mass extraction, as well as the development of the steam engine and metal forging completely changed the way goods were produced, exchanged and consumed.
Second Industrial Revolution
As the first industrial revolution, which began in the 19th century, in 1870 to be approximate, was driven by coal, the second revolution revolved around the discovery of electricity, gas and oil, in short various energy sources. The invention of the combustion engine went hand-in-hand with these fuel energy sources. Both steel and chemical based products entered the market during this time. Developments in communication technology got a jump start with the telegraph and later the telephone which brought in revolutionary changes in the way people communicated till then.
Third Industrial Revolution
During this era nuclear energy and electronics entered the landscape. Nuclear power generation began in Europe, grew in both Great Britain and the United States, then grew in Asia and is now an inevitable part of the world.
The Third Industrial Revolution began in the ’70s in the 20th century through partial automation of processes using memory-programmable controls and computers. Since the introduction of these technologies, we are now able to automate an entire production process or for that many commercial and non-commercial processes without much human assistance. Known examples of this are robots that perform programmed sequences of operations with lesser or no human intervention.
‘‘
Companies which understand technology can help in all areas of their businesses, including overall business strategy, workforce and talent strategies will succeed.
Emergence of Fourth Industrial Revolution
As we continue moving through the fourth industrial revolution, we see a shift to renewable energy such as solar, wind and geothermal due to commercial and societal factors; commercial because of the cost and the inevitable depletion of fossil fuel and societal because of the concern for the environment.
However, the momentum and power of Industry 4.0 come not from the shift in energy sources but from the acceleration of digital technology transformation in every sphere of our life, business and personal.
Though Industry 4.0 comprises of the transition from fuel energy to renewable energy sources which would be the future sources given the fact that fossil sources will not last long and also that it is major reason for greenhouse effect, climate change and other environmental hazards, and also nanotechnology, we will focus here more on the emerging technologies that normally come to anyone’s mind when we talk about Industry 4.0.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution refers to the marriage of physical assets and advanced digital technologies—the internet of things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, 3D printing, cloud computing, blockchain, big data, augmented reality (AR), mixed reality, nanotechnology, and more.
Some associate the benefits of the advancement in technologies mainly with efficiency, cost cutting, and profit maximizing. But the companies that are succeeding in this era are those that understand technology can help in all areas of their businesses, including overall business strategy, workforce and talent strategies, societal impact, and, of course, technological operations.
Industry 4.0 has the power to change the way that people work and do things. The digitalisation of the manufacturing environment allows for more flexible methods of getting the right information to the right person at the right time.
The increasing use of digital devices inside factories and out in the field means maintenance professionals can be provided with equipment documentation and service history in a timelier manner, and at the point of use or service. Microsoft HoloLens is a hardware/software tool that has made a difference in the way field service is delivered.
In short, Industry 4.0 is a game-changer, across industrial and non-industrial environments. The digitalization of manufacturing processes will change the way that goods are made, stocked, distributed, serviced and refined. With Industry 4.0, production shifts from a centralized to a decentralized model, symbolizing an impactful change in the traditional approach.
Let us discuss few of the most dominant innovation areas that influence the entire industry and life which will draw from the application and potential of the most disruptive of these technologies.
Big Data & Predictive Analytics
When it comes to Industry 4.0, data and analytics play a key role in creating value. Some studies have estimated that by leveraging the potentials of big data and analytics companies active in the field are able to reduce downtime by up to 45%, additionally increasing output by as much as 25%.
Big data is used increasingly for real-time decision making, while predictive analytics are very much useful due to their capability to foresee and/or predict the failure of a machine, thus acting as an enabler or trigger for preventive maintenance.
Predictive analytics will be followed by prescriptive analytics, which will suggest decision options to take full advantage of the results provided by predictive analytics. It is all about predicting problems, triggering action and providing solutions to the problems.
Cloud Computing
The importance of cloud computing will be understood when we realize that Industry 4.0 would not exist without it. Due to this technology enabling the handling of large amounts of data, which is needed to automate production processes, cloud computing serves as a key, if not indispensable, and element in the fourth Industrial Revolution.
Over time, cloud technologies are anticipated to improve even further, reaching extraordinarily short reaction and response times. Cloud computing is already in use in solution packages, some of which are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS).
To give an example, Microsoft provides its desktop applications like Office or Microsoft 365 as SaaS, its cloud computing environment or platform, Azure, as IaaS and its Business Applications like Dynamics ERP, CRM, Customer Engagement suite as IaaS. Google My Business, AWS cloud environment are other prominent examples of big players in cloud computing. Cloud models make it easy for organizations of any size and cash to adopt technology and pursue digital transformation because of the shift from Capex to Opex investment model.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, has undergone a substantial transformation over the last three decades. Its development has compelled usage of other materials than plastics to 3D print, including metal, ceramic and even biomaterial resulting in cost reduction, efficiency enhancement and environmental benefits.
Additive manufacturing changes the production process through which products are manufactured as it provides customers with the capacity and platform to co-create goods together with companies to their specific needs.
Cybersecurity
The connectivity Industry 4.0 brings with it also adds a layer of vulnerability. The increased exposure of organizations’ data and information due to connectivity means it is at high risk of falling victim to potential cyberattacks, forcing companies to increase the security level of their manufacturing lines.
Manufacturers who act proactively, facing challenges before they arise, will be rewarded with a vibrant, well-equipped ecosystem capable of securing their smart factories through innovative solutions. While this is a threat, this is a great opportunity for startups to come up with superior cyber security tools.
‘‘
Augmented Reality (AR) is powerful enough to increase the performances of both people and processes by 50 per cent by helping in reducing cost emerging from human error or inefficiency.
Predictive Maintenance
Manufacturers agree that, ideally, a machine should only be repaired when necessary, meaning at a point when a defect is affecting the machine’s performance, but where keeping it running is still safe until the company finds a convenient time slot for repair.
As one of the most hyped innovation areas, predictive maintenance is capable of generating considerable cost reductions, with the cost of repairs estimated to decrease by 12%, thus lowering the cost of planned repair by 30%. This includes reducing or eliminating down times thus shielding the company against the adverse effects on the overall growth.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality has reached the right maturity level for use in a productive environment like smart factories. This has already been proven to increase the performances of both people and process, thus helping in reducing cost emerging from human error or inefficiency.
In fact, some studies have seen that AR is powerful enough to improve performance by up to 50%. Some of the potential usage scenarios for AR in Industry 4.0 include Operations, Maintenance, Field Service, & Remote Assistance, Training, Quality Control as well as Safety Management.
The innovation areas outlined above are just a few of the crucial digital drivers that have been recognized in Industry 4.0 and also include Robotics, Simulation, Industrial IoT Platforms, Blockchain, and Artificial Intelligence.
We have been noticing that most businesses are beginning to try to find balance between profit and purpose, thanks largely to increased pressure from customers, employees, and other stakeholders.
With a market value of US$220 billion by 2022, companies keen on tapping the emerging opportunities are acting prudently. Industry 4.0 opens up unlimited potential opportunities for startups and small businesses in the technology domain. And new changes and opportunities are emerging every day
Deloitte did a survey recently on Industry 4.00 that took a closer look at which technologies business leaders anticipate will have the greatest impact on their organizations and has identified the internet of things, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data and analytics as those top four technologies. .
There is a strong correlation and dependency between several Industry 4.0 technologies and the power of the results comes from the convergence and collective use of them.

The pros of the fourth industrial revolution
Before we conclude, let us have a quick look at some of the benefits Industry 4.0 and its emerging trends bring to organizations and society as a whole.
- Higher productivity that contributes to profitability and growth of business
- Improved quality of life by way of, for example, ordering a cab, booking a flight, buying a product, making a payment, listening to music, watching a film and even controlling the lights and temperature in our homes
- Developing new markets through a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between physical, digital, and biological spheres” will create new markets and growth opportunities,
- Lower barriers to entrepreneurship. New technologies such as 3D printing for prototyping, the barriers between inventors and markets are reduced.
- Environmental and social benefits. Industry 4.0 implementation will reduce the emission of greenhouse gases. Electric cars and vehicles, powered by renewable energy sources, will be the classic example of how this will emerge.
The cons of the fourth industrial revolution
Like in anything in life, Industry 4.0 also suffers from perils. All of them are not just perils or cons but challenges too. Let us not skip them in this discussion.
- Inequality, It is all about who gets the benefits of these technologies and of the results they help produce.
- Cyber security. This is a very sensitive issue that is stopping many organizations from embracing Cloud and Industry 4.0
- Core industries disruptions. Taxis are competing against Ola and Uber, traditional television and cinema compete with Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hotstar and YouTube, the hotel industry with AirBnB or OYO and Mom-and-Pop and Kirana stores are competing against Amazon, Jio Mart or Flipkart..
- Ethical issues. With improved AI, genetic engineering, and increased automation, there are new ethical concerns and questions of morality that already differ greatly from individual to individual.
- Employees’ apprehensions. Industry 4.0 is expected to have a far-reaching impact on the employees as those jobs with a low degree of skills will be performed by automated robots. Employees losing jobs will create a demand slump which in turn will affect profitability and growth of the economy. It is not just about ethics but about the economy too.
- Socio-technical implications. Industry 4.0 is a socio-technical system. For the successful and sustainable implementation of Industry 4.0, the joint optimization of Socio-technical systems is desired.
Conclusion
So here we are on that edge of Industry 4.0 that radically impacts all spheres of our daily lives. It can be an era of economic and knowledge growth and improvements and advancements in the way we live, work, and even think but we also need to be wary of its potential to disrupt every walks of life and find ways to mitigate these risks. It is again a question of balancing its good and bad effects for the betterment of life of people from all sections of society.




