The total cost of production includes both fixed and variable costs. It is defined as the total expenditures incurred in production to purchase factor inputs including labour, land and capital that are needed to manufacture a product. Cost refers to the total cost incurred by a business to produce a specific quantity of a product or offer a service. These expenditures may include any kind of factor inputs like raw materials, human resources, capital machines, etc. For instance, production costs for baking a loaf of bread will include expenses like a microwave oven, raw wheat, sugar, baking powder, baker, and mass-producing the bread will require a place like a restaurant, bakery, etc. In the case of companies that offer services, they will require costs of setting up an office, material costs of setting up the services, payment to people who deliver the services and costs of delivering the services.
Types of Costs of Production
Every business incurs costs and receives revenue. A business runs only if the revenue or benefits of running the business is more than the costs incurred. In other words, a business is profitable only when costs are less than revenue. During the manufacturing process, a business will incur different types of costs depending on the product or service they offer. The following are the type of costs a normal business might occur regularly:
- Fixed costs
Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the amount of output produced. In other words, fixed costs remain constant even if the company produces zero output or maximum output. A bakery must pay its rent irrespective of the number of goods it produces. They will have to pay the same amount to purchase an oven and fridge even if the amount of goods they produce fluctuates over time. It is a fixed cost. Salaries paid to employees are also fixed costs. Fixed costs are fixed in the short-term. They become variable after a period of time depending upon the business.
- Variable costs
Variable costs are costs that change with the changes in the level of production. Variable costs increase with the increase in production and vice versa. If the production is zero, then no variable costs are incurred. In a bakery, variable costs include raw materials like sugar, wheat, cocoa powder etc. on the process and direct labour costs. If for instance, it costs Rs. 20 per pastry produced, then the total variable cost incurred by the bakery to produce 100 such pastries would be Rs. 2000.
- Total cost
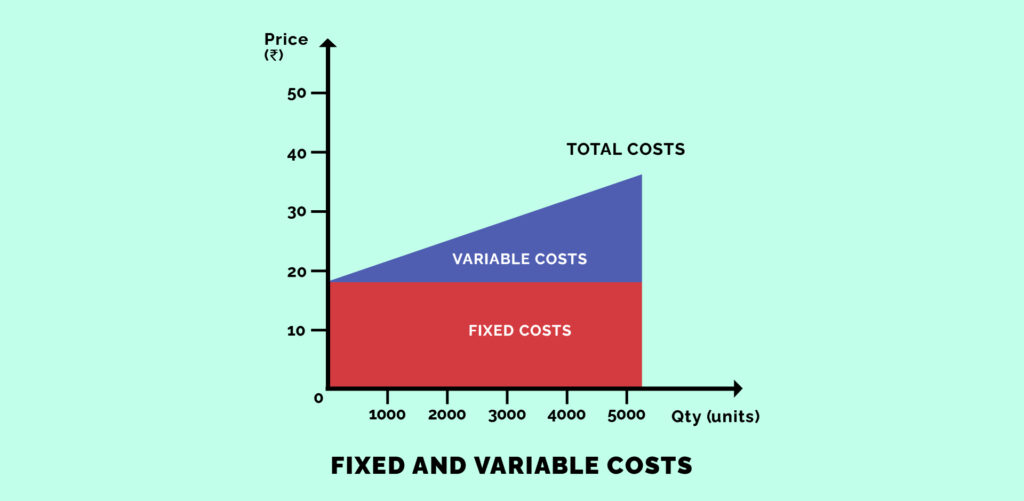
Total cost as mentioned before includes both variable and fixed costs. It takes into account all the costs incurred in the production process. For the bakery example, the total cost would include the cost incurred in buying the microwave oven, chairs, tables, renting the place and the amount spent on buying ingredients. If the fixed cost was Rs. 10,000 and the variable cost for producing 100 units of pastries was Rs. 2000 then the total cost of producing 100 pastries will be Rs. 12,000.
- Average cost
The average cost is defined as the total cost of production divided by the number of units produced. You can also calculate it by adding up the average variable costs and the average fixed costs. Average costs are used to decide product pricings for revenue or profit maximisation. The average cost per unit should always be minimised by the business so they can increase profit margins without raising the costs of production.
- Marginal cost
Marginal cost is the expenditure incurred in producing one additional unit of output. It reflects the increase in total cost due to an increase in production by one unit. As fixed costs remain unchanged irrespective of the level of production. So marginal cost can also be defined as the increase in variable cost due to an additional unit of the product being manufactured. If the company wants to increase production capacity, it will compare the marginal cost with the marginal revenue obtained by producing an additional unit. If marginal costs are more than the marginal revenue, the firm won’t go ahead with the production. Marginal costs are affected by various factors like price discrimination, externalities, information asymmetry, and transaction costs.
‘‘
Fixed costs are usually recurring, i.e you have to pay them again and again at certain intervals like interest or rents being paid per month.
More About Fixed Cost :
Fixed costs are considered an entry barrier for new entrepreneurs. In accounting and economics, fixed costs are expenses incurred by businesses that are independent of the level of goods or services produced by the business. They are also known as indirect costs or overhead costs. Fixed costs are usually recurring, i.e you have to pay them again and again at certain intervals like interest or rents being paid per month. Variable costs on the other hand depend on the quantity of product produced and change accordingly. You can predict fixed costs at the beginning of the year but you cannot predict variable costs as they depend on production levels.
For instance, in our bakery example, the monthly rent and phone line are fixed costs, utility bills are also fixed costs. These costs will be incurred irrespective of how much bread is produced and sold. Wage, wheat, sugar, electricity on the other hand are variable costs. With the increase in production, you will need more workers and more raw materials and your variable cost would increase accordingly.
Difference between Fixed Cost and Variable Cost:
It is necessary to know how costs divide between variable and fixed costs. This helps in forecasting the earnings generated by various changes in unit sales and thus reflects the financial impact of marketing campaigns. By definition, costs that vary or change depending on the company’s production volume are variable while costs that do not change concerning production volume are fixed. In recent years, fixed costs gradually exceed variable costs for many companies. This is because automatic production increases the cost of equipment, including the depreciation and maintenance and also it becomes cumbersome to adjust human resources according to the actual work needs in the short term thus making labour a part of fixed costs.
When the level of production increases, total variable costs increase and when the production level decreases, total variable costs decrease. On the other hand, total fixed cost remains constant irrespective of the change in the level of production.
Example for Fixed vs. Variable Costs incurred by a bakery
Depreciation of oven: Variable cost
Cost of shipping finished goods to customers: Variable cost
Wheat used in manufacturing bread: Variable cost
Baker’s and bakery manager’s salary: Variable cost
Electricity used in manufacturing: Variable cost
Packing supplies for shipping products: Variable cost
Advertising costs: Fixed cost
Insurance: Fixed Cost
Fixed Costs become Variable over time:
Fixed costs are not fixed permanently. They can and mostly will change over time. However, by contractual obligations, they are fixed over months or years. A company may have unpredictable expenses independent of production like renting a warehouse which is fixed over some time of contract. But there are no fixed costs in the long run. This is because all the short-run fixed inputs become variable in the long run.
Machines, buildings, rent etc cannot be changed in the short run based on production and therefore become fixed costs but over a longer period depending on the business, these investments can become variable like increase in the number of machinery, buildings, etc based on your overall level of production. Discretionary costs fixed costs are fixed annually like advertising, insurance premia, machine maintenance, and research & development expenditures.
‘‘
Machines, buildings, rent etc cannot be changed in the short run based on production and therefore become fixed costs but over a longer period depending on the business, these investments can become variable.
Fixed Costs and Business Planning:
Capital can be the fixed price for buying a warehouse for production machines and it can be a total salary paid to a particular quantity of labour. Based on the market and product, many things are covered under fixed costs and variable costs distinctively. However, if short term fixed costs are too high, firms may not enter the market. Thus these firms help a firm determine if they can enter a market.
In business planning and management accounting, fixed costs, variable costs are different as compared to their usage in economics. In accounting, fixed costs broadly include almost all expenses that are not included in the cost of goods sold, and variable costs are those captured in costs of goods sold. In order to create a balance between the two approaches, just assume that the accounting period is equal to the period in which fixed costs are independent of production. In reality, however, this equivalence does not always hold.




